Clinical Pharmacists
Information and resources to support Clinical Pharmacists in Primary Care.
What is a Clinical Pharmacist?
Clinical pharmacists work in Primary Care as part of a multidisciplinary team, in a patient facing role to clinically assess and treat patients using expert knowledge of medicines for specific disease areas. If they are recruited under the additional roles reimbursement scheme (ARRS), they must complete the 18-month Primary Care Pharmacy Education Pathway from the Centre for Pharmacy Postgraduate Education (CPPE). If they are not already independent prescribers, they can then complete an independent prescribing qualification.
They work with and alongside the general practice team, taking responsibility for patients with chronic diseases and undertaking clinical medication reviews to proactively manage people with complex polypharmacy, especially for the elderly, people in care homes and those with multiple comorbidities.
What do Clinical Pharmacists do?
- Clinical medication reviews for patients with single or multiple long – term conditions where medicines optimisation is required
- Reconcile medicines following discharge from hospitals or intermediate care and working with patients and community pharmacists to ensure patients receive the medicines they need post-discharge and to reduce the risk of readmission.
- Be involved in multidisciplinary clinical meetings within the PCN where appropriate
- Contribute to the provision of out of hours/on call/extended services for the practice and the patients. These can include patient facing and telephone consultations, signposting to other services and/or healthcare professionals where appropriate, while working within scope of practice and limits of competency.
- Manage repeat prescription requests, resolving queries where possible within scope of practice. To ensure patients have appropriate monitoring tests in place when required. • Implement changes to medicines in line with MHRA alerts, product withdrawal or shortage and other local or national guidance
- Maintain full and complete records of all patient contacts using appropriate clinical templates and coding
- Undertake a proactive role in audit and quality improvement implementing recommendations where appropriate.
- Provide independent information to patients with regard to medicines and prescribing changes, initiating further support from other healthcare professionals where appropriate
- Participate in review and setting of policies relating to medicines management and prescribing and help ensure practices prescribe in accordance with local guidelines and formulary
- Identify areas of clinical risk at network level and make recommendations to support the introduction of new working practices that will optimise the quality of prescribing and make more efficient use of network resources.
- Monitor network practices’ prescribing against the local health economy and make recommendations for GP’s or amend within scope of practice, based on findings.
- Maintain own clinical and professional competence and be responsible for own continuous professional development
- Work with practices to ensure full compliance with Care Quality Commission standards for safe and effective care
How do Clinical Pharmacists fit into the NHS Workforce?
Clinical pharmacists work as part of the general practice team to improve value and outcomes from medicines and consult with and treat patients directly, allowing improvement and increasing quality of patient care.
How do Clinical Pharmacists help the system?
Having clinical pharmacists in GP practices means that GPs can focus their skills where they are most needed, for example on diagnosing and treating patients with more complex conditions. This helps GPs to manage the demands on their time.
What training and qualifications do Clinical Pharmacists have?
- All pharmacists complete a 4-year undergraduate masters degree followed by a year of pre-registration training in pharmacy practice.
- Pharmacists frequently have post graduate diplomas in clinical pharmacy
- Clinical Pharmacists employed through the Network Contract DES will either be enrolled in, or been granted exemption from, the 18-month Primary Care Pharmacy Education Pathway (PCPEP). This pathway equips the pharmacist to be able to practice and prescribe safely and effectively in a primary care setting.
- All Clinical Pharmacists will be part of a professional clinical network and will always be clinically supervised by a senior Clinical Pharmacist and GP clinical supervisor.
- Independent prescribing is in addition to the training pathway and will be completed following completion of the PCPEP.
Pre-requisites
Pharmacy degree and registration as a pharmacist with the General Pharmaceutical Council.
Length of course
- 18-month pathway, including 28 days dedicated study days
- Learner receives a statement of assessment & progression on completion of the pathway
- No placement is required as the Clinical Pharmacist will be employed within primary care whilst completing the PCPEP.
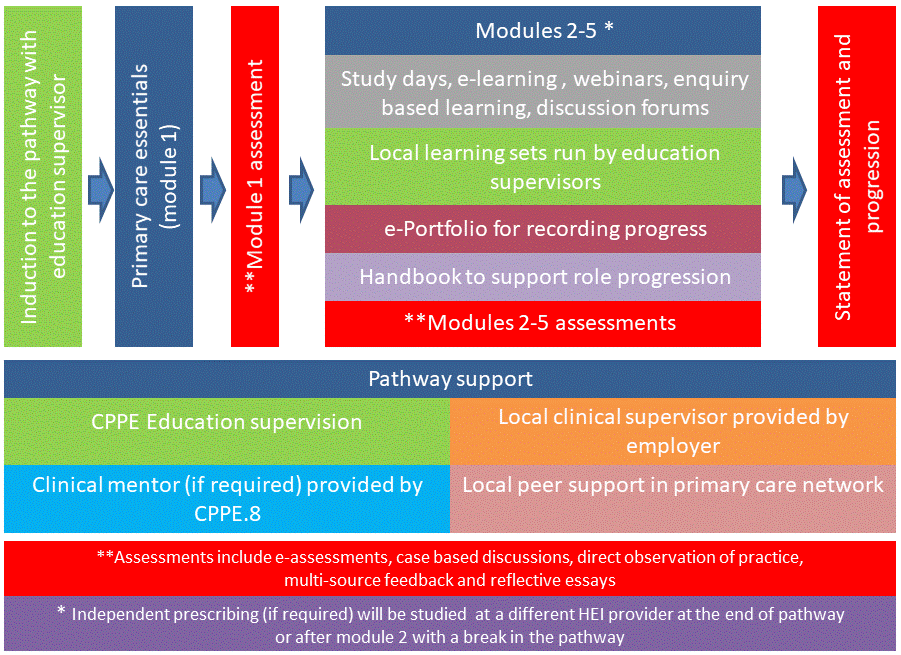
PCPEP (Primary Care Pharmacy Education Pathway)
CPPE is commissioned by Health Education England to deliver training to pharmacy professionals working in primary care as part of the primary care Network Contract Directed Enhanced Service (DES). The Primary Care Pharmacy Education Pathway has been developed to align the education requirements of pharmacists and pharmacy technicians with the NHS Long Term Plan and the primary care Network Contract Directed Enhanced Service. The 18-month pathway will equip pharmacists and pharmacy technicians with the necessary knowledge, skills and experience to work in various patient-facing roles in primary care networks as part of a multidisciplinary team. Pharmacists and pharmacy technicians will be able to access a range of different study methods to suit different learning styles, a continuous assessment process and support from supervisors and peers. Pharmacy professionals who are already enrolled on the General Practice Pharmacy Education Pathway (GPPEP) or the Medicines Optimisation in Care Homes (MOCH) Pathway (predecessor CPPE programmes) will continue with this, but any new applicants employed through the primary care Network Contract Directed Enhanced Service will join PCPEP.
Source: HEE Pharmacy Team
Useful Links:
NHS England
Expanding our Workforce - Clinical Pharmacists
NHS England
Clinical Pharmacy and Paramedics in Primary Care
Pharmacy Placement Programme with DeMontfort University (GPEP)
The LLRTH team is working in partnership with colleagues at DeMontfort University to deliver a placement programme in primary care for 120 pharmacy students. Ordinarily, the programme would run in a general practice setting, face to face, but some innovative changes have been made to ensure that students can still access a virtual programme to enrich their learning experience and provide them with an understanding of pharmacy in primary care during the COVID-19 pandemic. Each participating student accesses a 2 week programme in General Practice which includes consulting skills, an online consultation with a consenting patient, and presentation of findings.
Dr Amit Bharkhada, our Clinical Director of Strategy, is passionate about maximising educational opportunities in primary care: “this is an innovative programme that we have developed at pace with our DMU colleagues – already we are receiving positive feedback from students who are keen to engage and explore all that the experience has to offer”. The placement programme will be fully evaluated to ensure that the programme adds maximum value for students as part of their overall learning.
We use cookies to help provide you with the best possible online
experience.
By using this site, you agree that we may store and access cookies
on your device.
Find out about our cookies.
